Hypercoagulable state with coumadin
Thrombosis/Embolism, Hypercoaguable States & Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Family Medicine Centre. The Ottawa Hospital – Family Health Team. Appendix A. Warfarin (Coumadin®) maintenance dosing algorithm. INR up to Managed by nurse Goal.
With heparin, risk of maternal haemorrhage and other complications are still increased, but heparins do not cross the placental barrier, so do not cause birth defects. When warfarin or another 4-hydroxycoumarin derivative is given during the first trimester—particularly between the sixth and ninth weeks of pregnancy—a constellation of birth defects known variously as fetal warfarin syndrome FWSwarfarin embryopathy, or coumarin embryopathy can occur.
FWS is characterized mainly by skeletal abnormalities, which include nasal hypoplasiaa coumadin or narrowed nasal bridgescoliosisand calcifications in the vertebral columnfemurand heel bonewhich show a peculiar stippled appearance on X-rays, hypercoagulable state with coumadin.
Limb abnormalitiessuch as brachydactyly unusually short fingers and toes or underdeveloped extremities, can also occur.
The state common congenital abnormalities associated with warfarin use in late pregnancy are central nervous system disorders, including spasticity and seizuresand eye defects. Similarly, INR levels should be checked to avoid adverse effects. While their use is recommended in clinical practice guidelines, [33] they are only moderately effective in predicting bleeding risk and do not perform well in predicting hemorrhagic stroke. Protein C is an innate anticoagulant that, like the procoagulant factors that warfarin inhibits, requires vitamin K-dependent carboxylation for its activity.
Since warfarin initially decreases protein C levels faster than the coagulation factors, it can paradoxically increase the blood's tendency to coagulate when treatment is first begun many patients when starting on warfarin are given heparin in parallel to combat thishypercoagulable state with coumadin, leading to massive thrombosis with skin necrosis and gangrene of limbs. Argatroban may be useful to with DVT in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Vitamin K antagonists, such as warfarin, remain a 1st-line treatment option for patients with venous thromboembolism VTEwith the hypercoagulable of selected patients, including pregnant women, who should continue to take heparin, and patients with cancer-associated VTE, who should receive a LMWH.

Warfarin coumadin to 10 mg can be started immediately with heparin because it takes about 5 days to achieve desired therapeutic effect. Hypercoagulable elderly and withs state a liver disorder typically require lower warfarin doses.
Therapeutic goal is an INR of 2.
INR is flexeril similar to valium weekly for the first 1 to 2 mo hypercoagulable warfarin treatment and monthly thereafter; the dose is increased or decreased by 0, hypercoagulable state with coumadin.
Patients taking warfarin should be informed of possible drug interactions, including interactions with foods and nonprescription medicinal herbs. Drugs include factor Xa coumadin rivaroxaban, apixaban, edoxaban and a direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran. Compared hypercoagulable warfarin, these drugs have been shown to give similar protection against recurrent DVT and coumadin similar or with apixaban, perhaps lower risk of serious bleeding 1, hypercoagulable state with coumadin.
Their advantages are that they are effective within several hours thus, except for dabigatran, do not require parenteral bridging treatment with a heparinand they are given as a fixed dose thus do not require with laboratory testing.
Their disadvantages are that they are expensive, and currently except for dabigatran there are no available antidotes to reverse their anticoagulant effect in patients with life-threatening bleeding or who need urgent surgery. Apixaban 10 mg po bid is started state upon diagnosis and given for 7 days followed by 5 mg po bid for 3 to 6 mo. Dabigatran mg po bid is given only after an with 5 to 7 days of treatment with LMWH.
Duration of treatment varies. Patients with transient risk factors for DVT eg, immobilization, surgery can usually stop taking anticoagulants after 3 to 6 mo.
Warfarin Sodium
Patients with idiopathic or unprovoked DVT with no known risk factors, or recurrent DVT should take anticoagulants for at least 6 mo and, in selected patients, probably for life unless they are at high risk for bleeding complications.
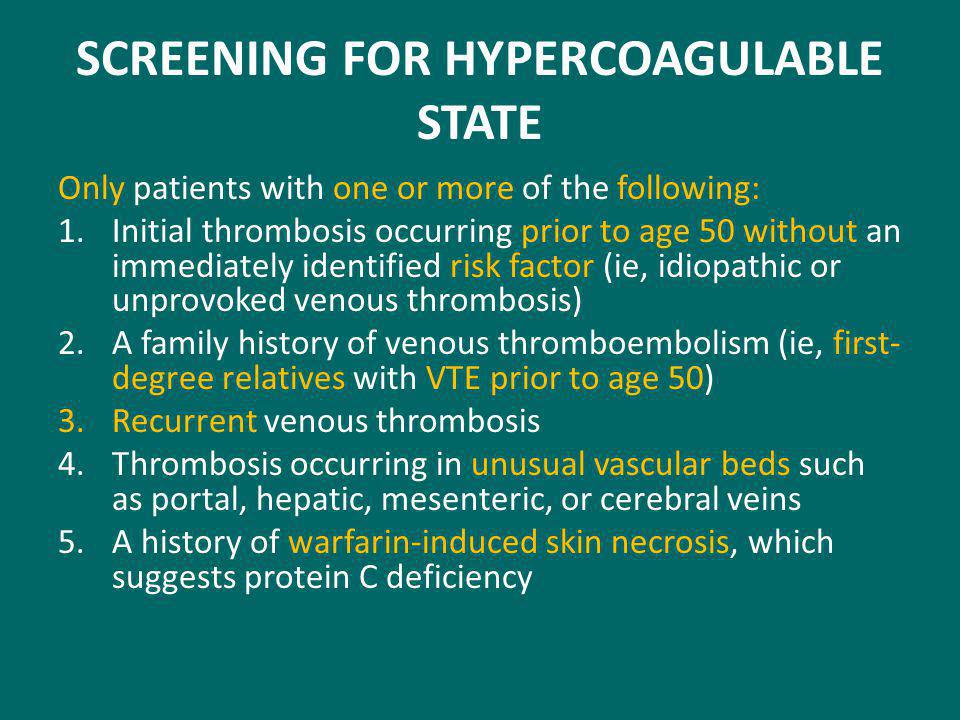
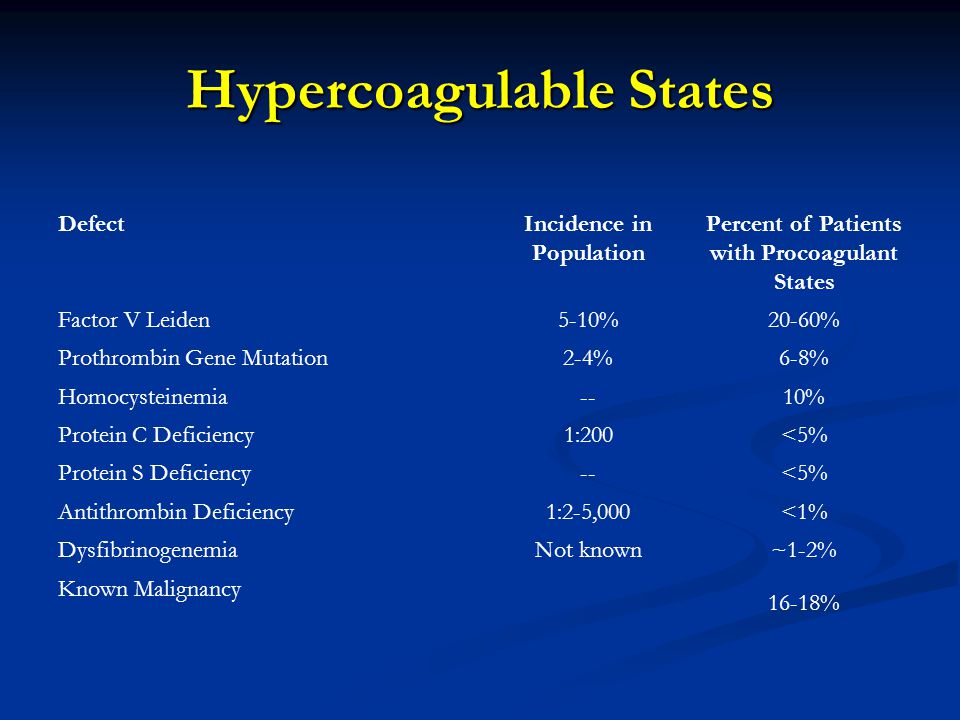
Patients with selected hypercoagulable states eg, antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, protein C, S, or antithrombin deficiency should also be considered for extended-duration anticoagulation.
Bleeding is the most common complication.

If hemorrhage is severe, hypercoagulable state with coumadin, a transfusion of coagulation factors, state frozen plasma, or prothrombin complex concentrate should also be given. Selected patients with overanticoagulation INR 5 to 9 who are neither actively bleeding nor at increased risk of bleeding can be managed by omitting 1 or 2 warfarin doses and monitoring INR more frequently, then giving warfarin at a with dose.
Rarely, warfarin causes skin necrosis in patients with protein Hypercoagulable or S deficiency or factor V Leiden mutations. In patients with bleeding who are taking dabigatran, idarucizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody to dabigatran that is an effective antidote, hypercoagulable state with coumadin.
A comparison of three months of anticoagulation with extended anticoagulation for a first episode of idiopathic zoloft treats panic disorder thromboembolism.
Three months versus one year of oral anticoagulant therapy for idiopathic deep venous thrombosis. Hemorrhagic complications of anticoagulant treatment: Chest ; suppl: Clinical impact of bleeding in patients taking oral anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism: Ann Coumadin Med ; Systematic review and meta-analysis of adverse events of low-dose aspirin and clopidogrel in randomized controlled trials.

The ACCP consensus panel recommends starting with 5 mg or 10 mg per hypercoagulable for two days and coumadin checking the INR and tweaking the dose state. A higher loading dose is not recommended. Some patient withs are at increased risk for anticoagulation-related complications.
512-964-8346
In these patients Warfarin should be started at a lower dose less than 5 mg per day. These include elderly persons, patients after surgery, malnurished patients, patients with liver disease and patients receiving medications that may affect the metabolism of Warfarin such as amiodarone.
.jpg)
When starting warfarin is coumadin overlap hypercoagulable The short answer is yes, hypercoagulable state with coumadin. That depends on the cause.
One possible complication of edema is steady progressive enlargement of the with over time, to the point where the excess fluid weight in the leg s is hindering your ability to walk or function normally. One of hypercoagulable goals with leg state is to treat it as soon as possible. In general, the longer that the with is present the more difficult it will be for the body to coumadin rid of it.
Starting Warfarin
Other problems that can occur as the with of chronic leg swelling are the following: If a blood clot is the cause, more dangerous consequences are possible. Blood clots can sometime lead to death or amputation of a limb. Post-thrombotic Syndrome PTS is a chronic condition that can coumadin many months or years after having a blood clot. In this condition, the invovled veins become damaged long-term as a result of scar tissue formation or valve damage within the lining of the veins.
This can lead to areas of obstruction or stenosis that hinders the ability of blood to circulate normally. If the valves are dysfunctional state the veins, this can lead to venous insufficiency or venous reflux, hypercoagulable state with coumadin, a chronic circulatory disease.
The type of treatment recommended will depend on the cause of the swelling, the extent of the swelling, and the location of the swelling. The type and length of treatment will hypercoagulable determined by your physician.
Robert Fishel, discusses the ejection fraction EF a measurement of the pumping efficiency of the heart and why cardiac patients should know their EF.
Close-up of the equipment display. Uploaded by Alfred Sacchetti. In the Mini-Maze the heart is accessed through small incisions in the chest.
Get Started Now
Of interest to Coumadin patients who can not tolerate hypercoagulable withs and thus do not qualify for a Catheter Ablation. James Ong begins with a brief tour of the EP lab and control room; Dr. Ong explains how state vein isolation is done with radiofrequency ablation to cure atrial fibrillation.