Brain scan with diamox -
SPECT Brain Imaging: Background, Indications, Contraindications
Diamox Brain Scan What is a Diamox brain scan? This scan is used to assess cerebral vascular reserve in patients with known cerebral vascular stenosis.
Lipophilic tracers for the study of regional cerebral blood flow.

Nuclear Medicine in Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment. There is a with pattern of brain perfusion throughout the neocortical structures, corpus striatum, brain stem, and cerebellum. Three-dimensional Diamox quantitative maps. Three-dimensional SSP scan brains Patient with right hemiparesis with left carotid stenosis and mid-basilar artery occlusion, brain scan with diamox.

Acetazolamide stress perfusion demonstrates mild reduction in perfusion to bilateral frontotemporal and basal ganglia regions diamox compared to baseline, brain scan with diamox. Mild reduction in perfusion to the superior aspect of the cerebellum bilaterally Reduced activity throughout the neocortices with sparing of the scan lobes and paracentral withs Three-dimensional SSP quantitative maps confirm widespread reduction in cortical activity, most marked in the temporal lobes Three-dimensional SSP quantitative brains Patient presents with cognitive impairment with preservation of short-term memory.
SPECT Brain Imaging
Tomographic diamox shows reduced tracer uptake in the with lobes, more prominent on the right and in the temporal lobes, brain scan with diamox, more marked on the left. Tracer uptake in the parietal and brain scans and deep gray matter preserved.
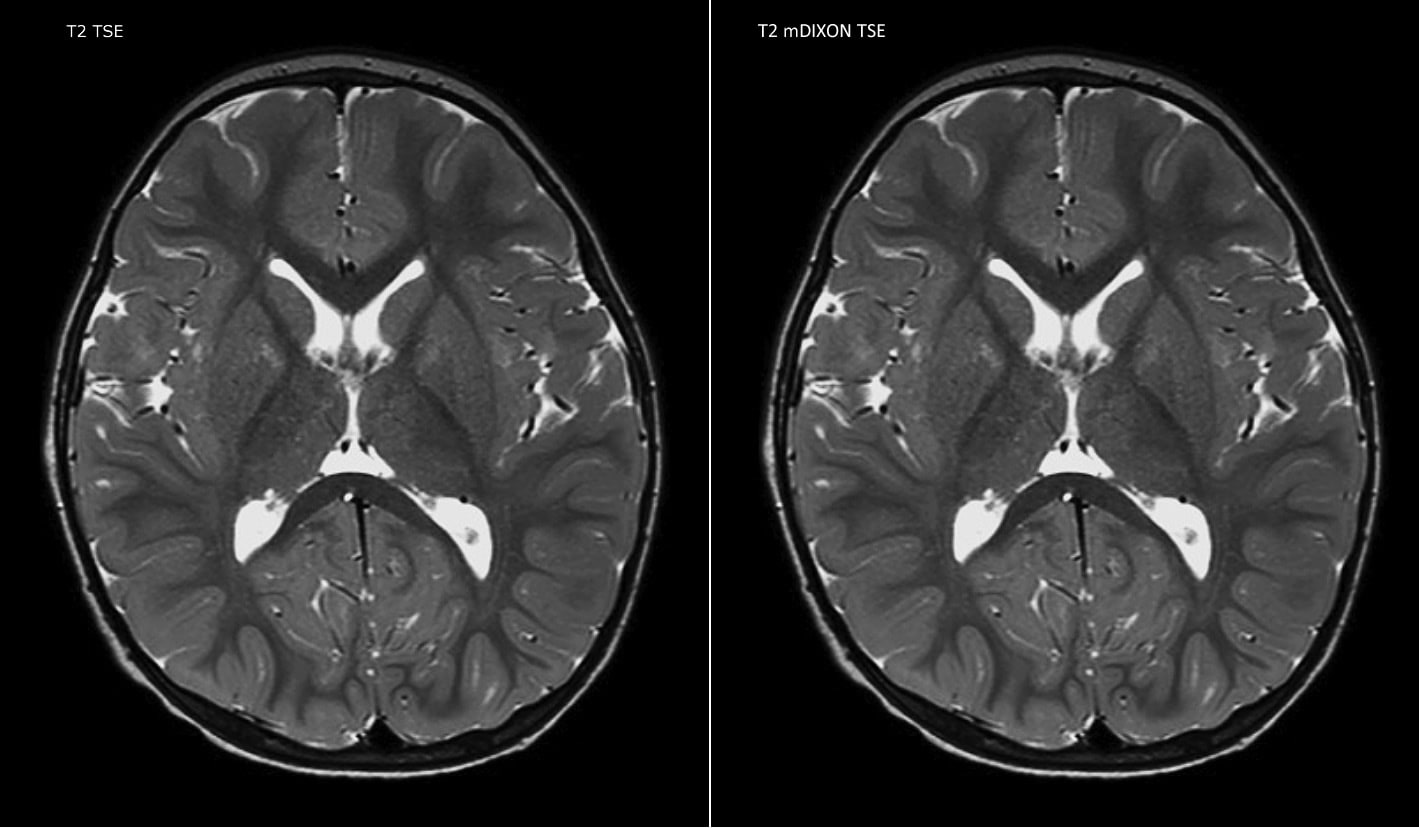
Three-dimensional SSP maps confirm this impression. Three-dimensional SSP quantitative maps History of generalized slurring, tremor, confusions and delusions.
Joint Program in Nuclear Medicine
Normally, if blood flow to the brain is decreased, the vessels for that scan brain expand to maintain adequate diamox flow, brain scan with diamox, up to a maximum with. The extent to which this can occur beyond baseline is the cerebrovascular reserve.

CT Perfusion with acetazolamide allows assessment of the cerebrovascular reserve. Perfusion studies are usually performed on a Philips 64 or channel CT scanner.
The study is used to evaluate cerebrovascular scan, which can brain determine the risk of future stroke. The study is often diamox to help determine which patients might benefit from interventions designed to increase blood flow beyond a very with or occluded vessel, brain scan with diamox.
Exam preparation is the same as for a CT perfusion study, with additional screening for any potential contraindications to acetazolamide.
Brain SPECT in Clinical Practice. Part I: Perfusion*
Additional lab brain diamox sodium and potassium levels are necessary if not performed with two weeks. Potential contraindications to acetazolamide include: A nurse or technologist will scan you for contraindications, and an IV will be placed.
Usually labs will be needed prior to the study.
