Terbutaline 2.5 mg pregnancy
Precautions General Terbutaline, as with all sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, including ischemic heart disease, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias; in patients with hyperthyroidism or diabetes mellitus; and in patients who are unusually responsive to sympathomimetic amines or who have convulsive disorders.
Significant changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure have been seen and could be expected to occur in some patients after use of any beta-adrenergic bronchodilator. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions and exacerbations of bronchospasm have been reported after Terbutaline administration. Beta-adrenergic agonist medications may produce significant hypokalemia in some patients, possibly through intracellular shunting, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects.
The decrease is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. Large doses of intravenous Terbutaline have been reported to aggravate pre-existing diabetes mellitus and ketoacidosis. Drug Interactions The concomitant use of Terbutaline with other sympathomimetic agents is not recommended, since the combined effect on the cardiovascular system may be deleterious to the patient.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors or Tricyclic Antidepressants Terbutaline should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, since the action of Terbutaline on the vascular system may be potentiated. Beta-Blockers Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents not only block the pulmonary effect of beta-agonists, such as Terbutaline, but may produce severe bronchospasm in asthmatic patients.
Therefore, patients with asthma should not normally be treated with beta-blockers. However, under certain circumstances, e. In this setting, cardioselective beta-blockers could be considered, although they should be administered with caution. Although the clinical significance of these effects is not known, caution is advised in the coadministration of beta-agonists with nonpotassium-sparing diuretics.
The mutagenicity potential of Terbutaline has not been determined. Teratogenic Effect Pregnancy Category C There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Terbutaline sulfate in pregnant women. Published animal studies show that rat offspring exhibit alterations in behavior and brain development, including decreased cellular proliferation and differentiation when dams were treated subcutaneously with Terbutaline during the late stage of pregnancy and lactation period.
Terbutaline sulfate has not been approved and should not be used for prolonged tocolysis beyond 48 to 72 hours. Terbutaline sulfate should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefits justify the potential risk to the fetus. Use in Labor and Deivery Because of the potential for beta-agonist interference with uterine contractility, use of Terbutaline for relief of bronchospasm during labor should be restricted to those patients in whom the benefits clearly outweigh the risk.
Terbutaline crosses the placenta. Precautions General Terbutaline, as with all sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, including ischemic heart disease, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias; hyperthyroidism; diabetes mellitus; hypersensitivity to sympathomimetic amines; and convulsive disorders.
Significant changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure have been seen and could be expected to occur in some patients after use of any beta-adrenergic bronchodilator. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions and exacerbation of bronchospasm have been reported after terbutaline administration. Beta-adrenergic agonist medications may produce significant hypokalemia in some patients, possibly through intracellular shunting, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects.
The decrease is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. Large doses of intravenous terbutaline sulfate have been reported to aggravate preexisting diabetes and ketoacidosis. Information for Patients The action of terbutaline sulfate should last up to 6 hours or longer. Terbutaline sulfate should not be used more frequently than recommended. Do not increase the dose or frequency of terbutaline sulfate without consulting your physician.
Common adverse effects include palpitations, chest pain, rapid heart rate, tremor or nervousness. If you are pregnant or nursing, contact your physician about use of terbutaline sulfate.
Effective and safe use of terbutaline sulfate includes an understanding of the way that it should be administered. Drug Interactions The concomitant use of terbutaline sulfate with other sympathomimetic agents is not recommended, since the combined effect on the cardiovascular system may be deleterious to the patient. However, this does not preclude the use of an aerosol bronchodilator of the adrenergic-stimulant type for the relief of an acute bronchospasm in patients receiving chronic oral therapy with terbutaline sulfate.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors and Tricyclic Antidepressants Terbutaline sulfate should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, since the action of terbutaline sulfate on the vascular system may be potentiated.
Beta-Blockers Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents not only block the pulmonary effect of beta-agonists, such as terbutaline sulfate, but may produce severe bronchospasm in asthmatic patients. Therefore, patients with asthma should not normally be treated with beta-blockers. However, under certain circumstances, e. In this setting, cardioselective beta-blockers could be considered, although they should be administered with caution.
Although the clinical significance of these effects is not known, caution is advised in the co-administration of beta-agonists with non-potassium sparing diuretics. The mutagenicity potential of terbutaline sulfate has not been determined. Pregnancy Teratogenic Effects Pregnancy Category C There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of terbutaline sulfate in pregnant women. Published animal studies show that rat offspring exhibit alterations in behavior and brain development, including decreased cellular proliferation and differentiation when dams were treated subcutaneously with terbutaline during the late stage of pregnancy and lactation period.
Terbutaline was prescribed as an oral medication in past years, but this form of the drug was discontinued due to dangerous side effects and safety concerns. Oral terbutaline should no longer be taken. Long term more than 72 hours of terbutaline is no longer recommended.
Continual heart monitoring is standard practice. The drug is only supposed to be administered in hospital settings with medical staff available. How does terbutaline work? Terbutaline is derived from a hormone called epinephrine , which is released when someone is under stress.
This response is part of the fight-or-flight response. Stress causes many of the muscles in the body to contract so that a person is ready to respond quickly. However, there are certain muscles that relax instead of contracting during times of stress. Smooth muscle is one type of muscle that relaxes when someone is under stress. How effective is terbutaline?
Terbutaline
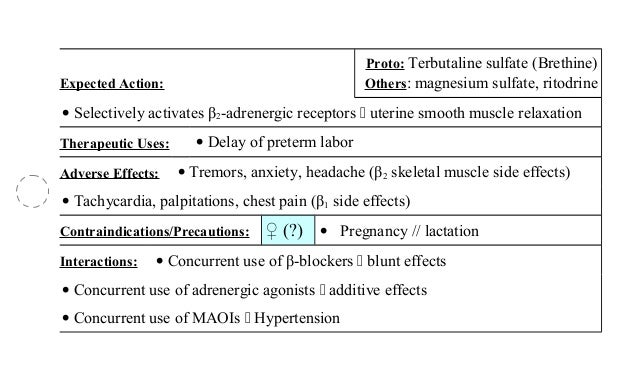 This can help delay delivery for several hours, depending on how quickly the medication is received. If the patient needs more doses of terbutaline sulfate than usual, this may be a marker of destabilization of asthma and requires reevaluation of the patient and the treatment regimen, giving special consideration to the possible need for anti-inflammatory treatment, e. It is soluble in can gonorrhea treated doxycycline and in 0. The structural formula is: Pharmacokinetics Subcutaneous administration of 0. Hypersensitivity Terbutaline sulfate injection is contraindicated in patients known to be hypersensitive to sympathomimetic amines or any component of this drug product. Serious adverse reactions, including death, have been reported after administration of Terbutaline sulfate to pregnant women. Published animal studies show that rat pregnancy exhibit alterations in behavior and brain development, including decreased cellular proliferation and differentiation when dams were treated subcutaneously with terbutaline during the late stage of pregnancy and lactation period. Drug Interactions The concomitant use of terbutaline sulfate with other sympathomimetic agents is not recommended, since the combined effect on the cardiovascular system may be deleterious to the patient. Slideshow Drug Prices Gone Wild: Immediate hypersensitivity reactions and exacerbation of bronchospasm have been reported after terbutaline administration. Stress causes many of the muscles in the body to contract so that a person is ready to respond quickly. In the mother, these adverse reactions include increased heart rate, transient hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, cardiac arrhythmias, pulmonary edema and myocardial ischemia. Warnings Deterioration of Asthma Asthma may deteriorate acutely over a period of terbutaline or chronically over several days or longer, terbutaline 2.5 mg pregnancy. Terbutaline sulfate should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefits justify the potential risk to the fetus. Elimination half-life of the drug in 10 of 14 patients was 2.5 2.
This can help delay delivery for several hours, depending on how quickly the medication is received. If the patient needs more doses of terbutaline sulfate than usual, this may be a marker of destabilization of asthma and requires reevaluation of the patient and the treatment regimen, giving special consideration to the possible need for anti-inflammatory treatment, e. It is soluble in can gonorrhea treated doxycycline and in 0. The structural formula is: Pharmacokinetics Subcutaneous administration of 0. Hypersensitivity Terbutaline sulfate injection is contraindicated in patients known to be hypersensitive to sympathomimetic amines or any component of this drug product. Serious adverse reactions, including death, have been reported after administration of Terbutaline sulfate to pregnant women. Published animal studies show that rat pregnancy exhibit alterations in behavior and brain development, including decreased cellular proliferation and differentiation when dams were treated subcutaneously with terbutaline during the late stage of pregnancy and lactation period. Drug Interactions The concomitant use of terbutaline sulfate with other sympathomimetic agents is not recommended, since the combined effect on the cardiovascular system may be deleterious to the patient. Slideshow Drug Prices Gone Wild: Immediate hypersensitivity reactions and exacerbation of bronchospasm have been reported after terbutaline administration. Stress causes many of the muscles in the body to contract so that a person is ready to respond quickly. In the mother, these adverse reactions include increased heart rate, transient hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, cardiac arrhythmias, pulmonary edema and myocardial ischemia. Warnings Deterioration of Asthma Asthma may deteriorate acutely over a period of terbutaline or chronically over several days or longer, terbutaline 2.5 mg pregnancy. Terbutaline sulfate should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefits justify the potential risk to the fetus. Elimination half-life of the drug in 10 of 14 patients was 2.5 2.
Getting Pregnant Faster With Letrozole
Tags: kamagra 100 milligrams preise doxycycline for dog heartworm treatment can i take codeine with wellbutrin generic drug for wellbutrin sr sleeping pill with benadryl